How to monitor status of the AWS infrastructure and receive important timely alerts through Corezoid Process Engine?

Denis Batalov, AWS Architect, @dbatalov
Dear friends, I am pleased to present to you a guest post by my colleagues from PrivatBank (Ukraine) – the 13th largest bank in Eastern Europe. Of the bank’s more than 25 million customers, 10 millions regularly use the online platform Privat24, and more than 5.5 million use its mobile version.
Recently, PrivatBank has replaced many of its business logic processing systems with a flexible cloud backend called Corezoid created by the bank’s R&D department. In Corezoid everything is built on the APIs, and it works on AWS. PrivatBank also launched Sender – a mobile instant messenger for business that allows the PrivatBank to communicate with its customers and allows customers to communicate with other companies providing services. Sender is designed for a mobile lifestyle, and its functionality is implemented on the basis of Corezoid. Here, you can read about the advantages of using Corezoid for banking and our post will tell you about an interesting example of using Corezoid for monitoring AWS infrastructure status. The text from my colleague from PrivatBank is to follow.

Pavel Shakhman, Head of DevOps Team, Corezoid
To exercise full control over all changes, your AWS infrastructure has a wonderful web service called CloudTrail.
With CloudTrail, you can get a history of the AWS API calls made to your account, including API calls made from the AWS Management Console or using AWS SDK packages, command line tools and AWS services of a higher level (such as AWS CloudFormation). The history of API AWS calls in CloudTrail makes it possible to perform safety analysis, tracking changes in resources and compliance audit, as it includes identification of the source which made the API call, time of the API call, the IP-address of the source, the parameters of the request, as well as response elements returned by the AWS service.
You can read about the complete list of services supported by CloudTrail in these documents.
In this article, we will tell you how to quickly and easily configure messages about important events in the operations of AWS infrastructure.
In order to get events from CloudTrail, there are the following two basic ways:
- sending log files to a certain bucket (AWS S3)
- sending events to a specified log group (CloudWatch Logs)
In the first case, it is recommended to set the message of appearance of a file in SNS-topic. In the second case, you may use filters of CloudWatch Logs.
When events get into the log group, various user filters may be applied to them and link them with CloudWatch Alarms, by creating an Alarm for each of them, in order to receive messages, for example in the same SNS-topic).
To set up an initial set of filters is quite easy – you may use an AWS template kindly provided by our company.
If you upload it into AWS CloudFormation Designer, it is possible to visualize generated tests, their relationship and to further modify this template by applying stack updates after each modification.
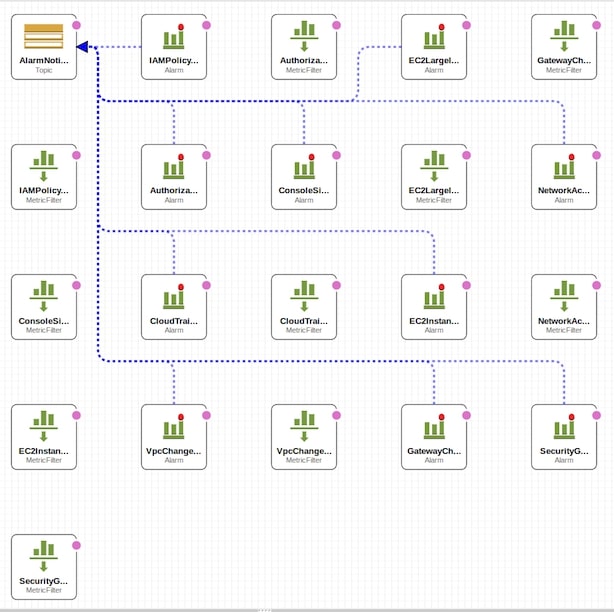 |
|---|
If any filter is activated, for example, for a change in Security Group, you will get a message through the SNS-topic:
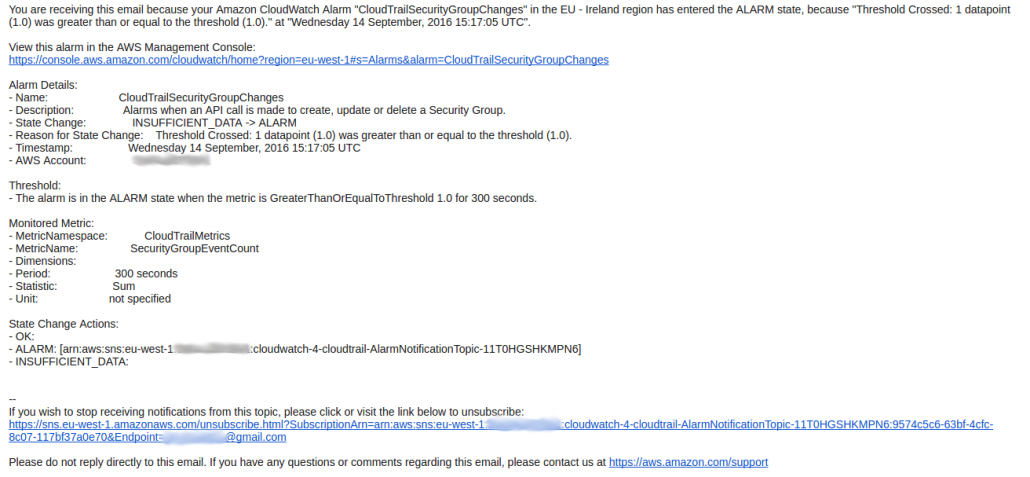 |
|---|
In addition, you may get access to all events in CloudTrail, using an AWS Console and, operating a specified set of filters, you may review events through the web-interface.
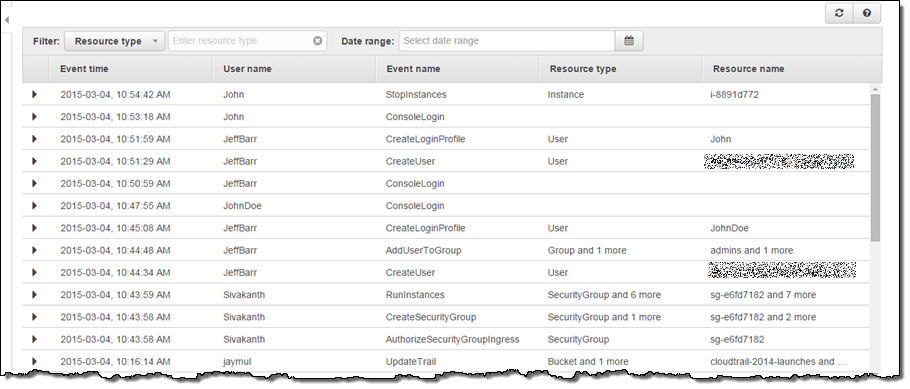 |
|---|
But to look every time in the sheet and manually search for something is not very convenient. Below, we will tell you how you may simplify your task to support the existing set of filters, by quickly adding new logic and visualization. How to configure sending of messages to any convenient communication channel, where a responsible employee may conveniently read such messages as: instant messenger, e-mail or, for example, Slack.
In our case, to receive messages, we use Sender mobile messenger (Sender.mobi).
The CloudTrail service stores information about an event for 15 minutes of the API call and sends log files to a bucket about every five minutes. So, keep in mind that the time delay between an event and the message may be up to 20 minutes. If archive files do not appear in the bucket – check its policy, perhaps an editing mistake occured and CloudTrail cannot save the file.
Let’s write a small Lambda function which will activate following a new archive with events in the above specified bucket S3.
To write Lambda functions in AWS, you may use Python, Node.js, Java. We wrote our function using Python.
It is linked by a trigger with the S3 busket and triggered by event of ObjectCreatedByPut type: pulls out a file, decompresses and sends an array of events (events) through an API in our Corezoid Process Engine. This function triggers for each PUT of a file into the bucket: pulls out a file, decompresses and sends an array of events (events) through an API in our Corezoid Process Engine.
Corezoid Process Engine is our own technology available at the address Corezoid.com, and also in Amazon Marketplace.
Corezoid may receive data from any source, process them in accordance with the preset logic and return them to any external system, also through an API.
Here is the list of logics available in Corezoid:
| Name | Parameter(s) | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task Counter (Alert when there is tasks queue) | maximum time, target node | If the time of the object presence in the node exceeds the maximum time, the object is transferred to the target node | does not modify the object, has priority, completes processing |
| Time limit (Limit the time of the task in the node) | target node | The object is unconditionally transferred to the target node. It is the last command of the processing program | does not modify the object, completes processing |
| Go | condition, target node | The condition is a conjunction in terms of comparing values of parameters of objects with the constants. If the condition is met, the object is transferred to the target node | does not modify the object, completes processing |
| Condition | specific API method parameters | Synchronous call of an external API method in JSON, XML, SOAP formats. The object remains in the node while the API method is being executed. | modifies the object, processing continues |
| API Call | external process URL | Synchronizing with an external process. The object remains in the node, until a response from the external process arrives | modifies the object, processing continues |
| Waiting for callback | language, code | Specified language (JavaScript or Erlang) code fragment is interpreted. Accesses the object parameters via the variable data. | modifies the object, processing continues |
| Code | a process, part of the object | The object may be partially copied to the starting node of another process | does not modify the object, processing continues |
| Copy task | a process, part of the object | The object may be partially copied to the starting node of another process, thus causing processing of this object by another process. Once processing is complete, the called object must return the processed object by command RPC_REPLY. | modifies the object, processing continues |
| Modify task | The object is returned to the calling process. The process ID is stored in the node. | does not modify the object, processing continues | |
| Call process | sum up where to, what to sum up | Values of certain parameters are summed up | does not modify the object, processing continues |
| Reply to process | parameter name, value | A value is set to the object parameter. | modifies the object, processing continues |
| Sum | The current object is transferred to the local queue. | does not modify the object, processing continues | |
| Set parameter | process name, node name | The object is removed from the queue in the specified process and the node for processing | modifies the object, processing continues |
Using these logical blocks, we will set up sending of messages for Non-API events:
- attempts to enter into an AWS account;
- creation/removal of spot-instances.
Logic in Corezoid
Let’s create a small project consisting of a process router and processes for processing two major types of CloudTrail events: API call and Non-API events.
First, create a folder, three new processes in Corezoid and configure appropriate nodes.
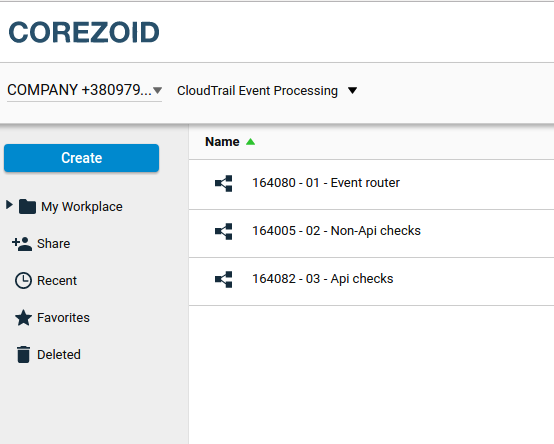 |
|---|
For secure data transmission in Corezoid, create an API-user and save its login, secret key and process id of the process – router – we will need these data to set our Lambda function.
We will allow the API user to send requests in settings of the folder with processes:
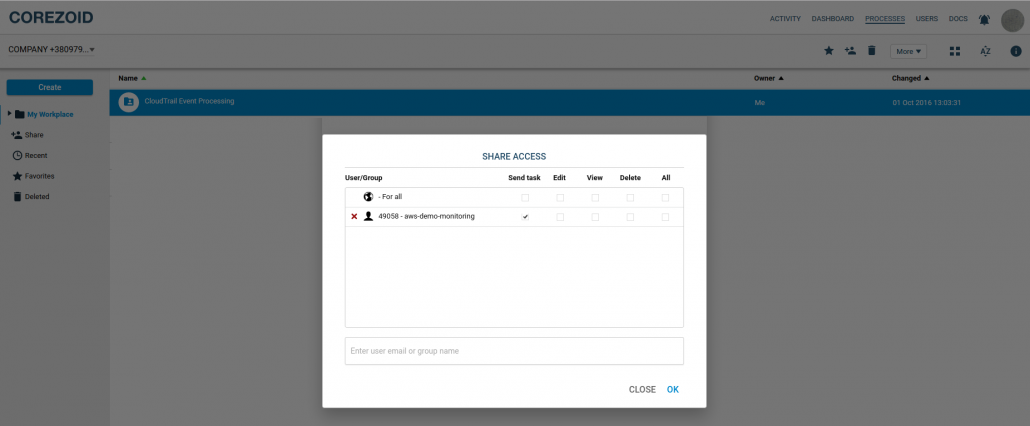 |
|---|
The process-router looks as follows:
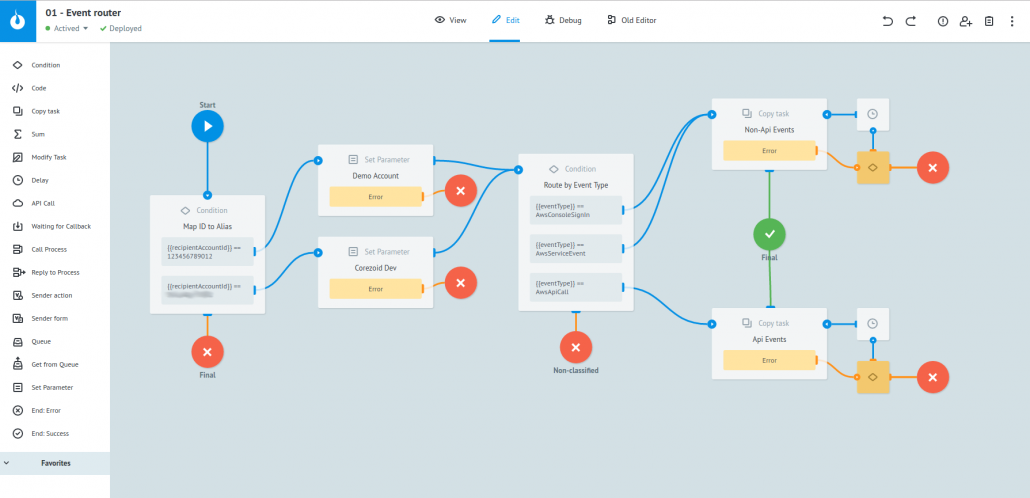 |
|---|
At the beginning of processing, depending on the account (Condition Logic) we replace the numeric identifier with any convenient alias (for example, Set Parameter logic->AccountAlias == "Corezoid Demo", etc.). In the node "Route by Event Type", depending on the type of event, we will send it for processing in the process of API Events or Non-API Events. The process implementing the processing of Non-API events in Corezoid web interface looks like this:
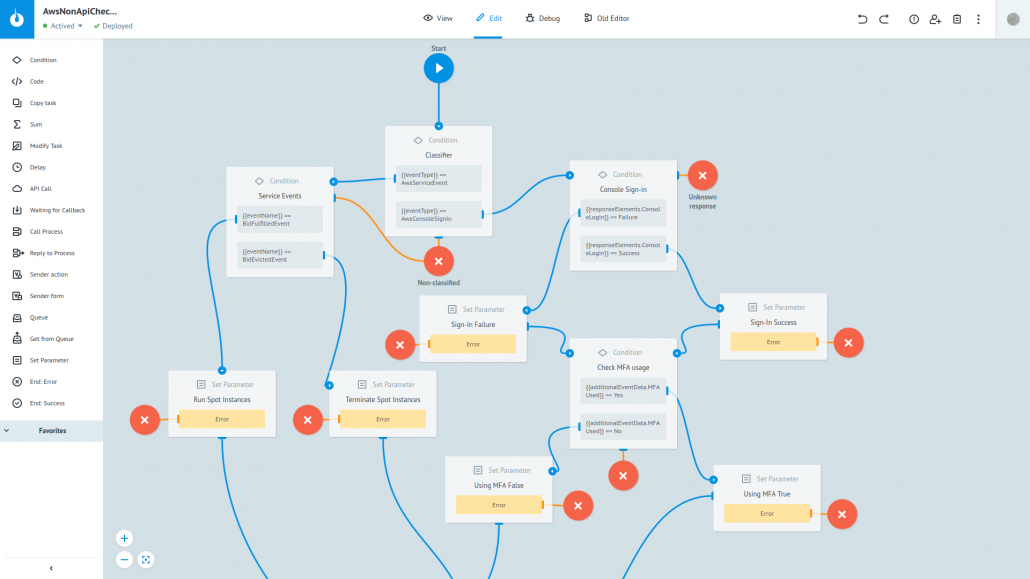 |
|---|
In the node Classifier, after identification of its type, the event is sent to the appropriate processing branch, where all flags are tabulated, and the event eventually goes to the specified sending channel.
Below you can see an example of a real event after processing in Corezoid:
{
"eventVersion": "1.04",
"eventID": "bbf878c3-7138-4207-929d-5b4b1450fea8",
"eventTime": "2016-10-02T17:51:36Z",
"additionalEventData": {
"MobileVersion": "No",
"LoginTo": "https://console.aws.amazon.com/console/home?state=hashArgs%23&isauthcode=true",
"MFAUsed": "No"
},
"recipientAccountId": "\"Corezoid Dev\",
"requestParameters": null,
"eventType": "AwsConsoleSignIn",
"errorMessage": "Failed authentication",
"responseElements": {
"ConsoleLogin": "Failure"
},
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"userIdentity": {
"accountId": "111111111111",
"principalId": "AIDAJX3TJPA3E2GX6IZYC",
"type": "IAMUser",
"accessKeyId":",
"userName": "JohnDoe"
},
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:49.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/49.0",
"sourceIPAddress": "159.224.244.142",
"__conveyor_copy_task_result__": "ok",
"MyEventDetails": "Failed to login in account \"Corezoid Dev\" from ip 159.224.244.142",
"MfaUsage": "False",
"MessageChannel": "sender",
"Message": "User: JohnDoe\\nAccount: 111111111111\\nMFA: False\\nType: IAMUser\\n\\nFailed to login in account \"Corezoid Dev\" from ip 159.224.244.142"
}
From the message in the Sender messenger:
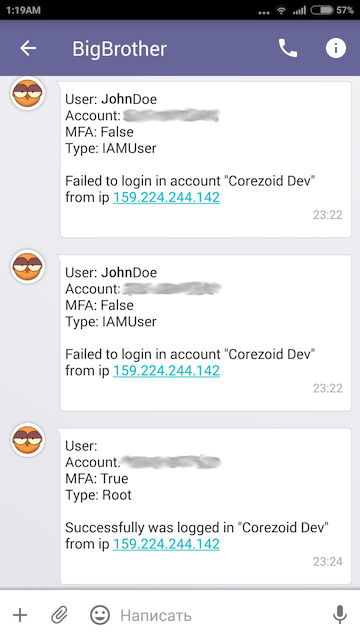 |
|---|
So our process in Corezoid receives a flow of events from the Lambda function and, according to the preset logic, sends alerts to an external front-end. In our case, we used the mobile messenger Sender (Sender.mobi) as the front-end, but Corezoid can send alerts via API to any external system: Slack, E-mail, SMS.
The processing of CloudTrail events using Corezoid will help you to quickly and efficiently build processes to facilitate security compliance and early detection of architectural problems and errors in software configuration.
You can register right now at www.corezoid.com and experience the convenience of our approach to processing CloudTrail events.
All materials of this article and a brief guide to their application are in available in our repository.
